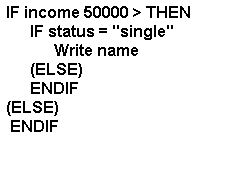Chapter 3 Assignment Page 2
Nested pattern
The nested pattern is used when several
related decisions need to be made. A nested pattern means there is another
decision on the true or false path of one decision. The second decision
is considered to be nested within the first decision. There is no limit
on the number of levels of nesting. A nested pattern is needed, when checking
the same field for more than two choices or when checking different fields
and the outcome of one decision has a bearing on the outcome of the other
decision. If a decision is made on the false path of one decision, the
next decision is performed only if the result of the previous decision
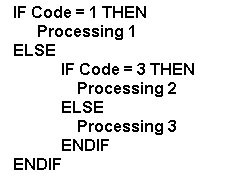
is false. For example: If you are checking for several codes. You
have a choice of code 1, code 2 or code 3. If you know the code is 1 then
there is no reason to check for code 2 or code 3. Therefore, if the result
of the decision CODE = 1 is true then the next decisions are not performed.
If the result of the decision CODE = 1 is false then the next decisions
are performed. If a decision is made on the true path of one decision,
the next decision is performed only if the result of the of the first decision
is true. For example: If you are checking the income and marital
status of a certain person. You want to output all people that earn more
than $50,000 and are single. If the decision income > $50,000 is true then
you need to check the marital status to see if they are also single.
NOTE: To connect the decisions
with a nested solution, start with the last decision listed and connect
the true path and false path together. Work your way to the top of the
nested structure until all the decisions are connected. The number of connector
symbols in the flowchart and the number of decision symbols will match.
In pseudocode, the number of IF, THEN and ENDIF statements will match and
line up.
In pseudocode:
In pseudocode:
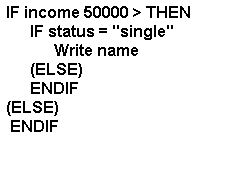
3. Problems using the Sequential
pattern –
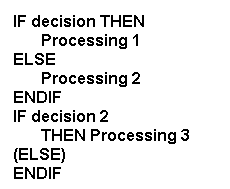
The sequential pattern is used when
more than one decision needs to be made and the outcome of one decision
has no bearing on the outcome of another decision. All decisions are made
one after the other. There is a separate IF, THEN, ELSE and ENDIF for each
decision.
In pseudocode:
4. Difference between the
problems solved using Sequential and Nested IF patterns.
Some problems can be solved using
both Sequential and Nested IF patterns. When given a choice, since fewer
decisions may be performed, using the nested control pattern is more efficient
than using the sequential pattern. When you are solving problems 15, 16,
17 and 18 in the textbook on pages 58 – 59, you need to decide whether
the problems work with the Sequential and Nested IF patterns and which
method is more efficient. You need to decide if problems #13 and #14 on
page 58 can be solved using a sequential structure. If not why? NOTE:
The
problems that involve asking an additional question on the true path need
to be solved using the Nested IF structure. They can be solved sequentially
if you use a program switch to indicate the value of the previous decision.
The problems that involve asking an additional question on the false path
can be solved using a Sequential pattern, but the solution is not as efficient.
Sequential Pseudocode Example:
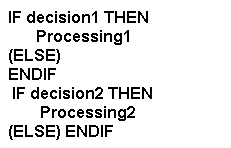
Sequential Flowcharting Example:
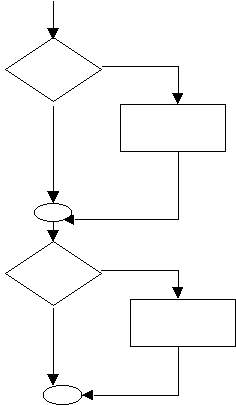
Pseudocode Example:
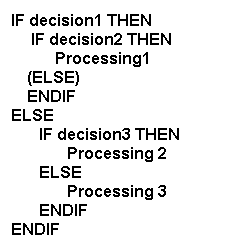
Flowchart Example:
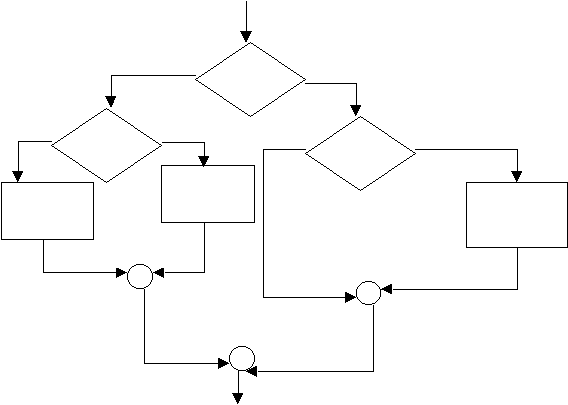
Exercises:
Problem #13 – To solve this
problem, the students need to think of the number line from math. How do
you know if a number is positive or negative? A positive number is greater
than zero and a negative number is less than zero. This is a nested problem
because there is one field (Number) with more that 2 choices (positive,
negative and zero).
Problem # 14 – This problem
is nested because there are two fields (height and weight) and the decisions
for the height and weight are related.
Problem #15 – This problem is
nested because it is checking the field (job code) for more than two choices.
Problems # 16 & 17 – These
problems are excellent problems to use to study for the final exam.