|
|
| Goal I. Second Law of Thermodynamics,
Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal I,
you must be able to:
- understand the
Second Law of Thermodynamics and the Third Law of Thermodynamics.
- understand entropy,
disorder, spontaneity and work (sample and follow-up problems 20.1, 20.2, and 20.3).
- describe how reaction spontaneity is governed by the thermal energy changes and
the entropy changes within the system;
- understand free
energy (G), work and the relationship between
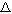 G° and the spontaneity of a process. Solve for G° and the spontaneity of a process. Solve for  G° given the data for G° given the data for  H° and H° and  S° (sample and follow-up problems 20.4). Read and understand Table 20.1. S° (sample and follow-up problems 20.4). Read and understand Table 20.1.
[Top]
| Goal
II. Determine and use oxidation numbers to analyze oxidation-reduction reactions. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal II,
you must be able to:
- determine the oxidation
number for each of its constituent elements given a chemical species (compound
or ion).
- use a periodic table
to predict the range of oxidation numbers for a given element and relate the
range of observed oxidation numbers for an element to chemical properties.
- relate the Stock
system and IUPAC nomenclature of oxo-acids and their salts to oxidation
number.
- balance redox equations
using the half-reaction method:
identify the species oxidized and the species reduced
in an oxidation reduction reaction and identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agent,
[Top]
| Goal III. Understand and
apply the principles underlying the use of chemical reactions to supply
electrical energy. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal
III, you must be able to:
- given the components of a spontaneous redox reaction,
diagram
a voltaic cell formed from these components and label completely as in
Figure 21.5.
- translate a given
redox reaction into a cell diagram and vice versa.
- define electromotive
force (emf) and describe the conditions
under which emf is equal to the standard cell potential, E°.
- describe the standard
hydrogen electrode (SHE) and know:
- the convention agreed upon for this electrod
- how SHE has been used to derive a table of standard
reduction potentials.
- use standard reduction
potentials to:
- identify and/or design spontaneous redox reactions
- calculate standard cell potential;
- alculate cell potential for non-standard reagent concentrations using the Nernst equation.
- understand
the key features of the dry cell, alkaline dry cell, lead storage
battery and the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell.
- explain corrosion
and how it is prevented with emphasis on the corrosion of iron and steel
products.
[Top]
| Goal IV. Understand and
apply the principles underlying the use of electrical energy to bring about
desirable nonspontaneous chemical reactions. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal
IV, you must be able to:
- use a table of standard
reduction potentials to predict the products of electrolysis in an electrolytic
cell.
- perform stoichiometric
calculations for electrochemical reactions.
- recognize applications
of electrolysis to production and purification of active metals and electroplating.
[Top]
|
Unit 5 Assignments
|
Objectives
1 through 3
Text:
Video Program: |
Chapter 20: pp 864-894;
No video tape for this chapter. |
Objectives
4 through 7
Text:
Video Program: |
Chapter 4: pp. 150-154; Chapter 21,
pp. 903-908.
18. Redox reactions |
Objectives
8 through 17
Text:
Video Programs: |
Chapter 21: pp. 908-949.
19. Voltaic cells
20. Electrolytic cells |
| Textbook
Assignments: |
Read and
Understand all "Sample Problems," "Follow Up Problems" and select any 5 blue-colored problems at the end of the chapters.
The answers
for the Follow Up Problems are at the end of the chapter; the answers for
the blue-colored problems are in Appendix E. |
| Mandatory ChemSkill Builder Assignments to be submitted for grade (Scores of 80% or higher on each section will receive full credit): |
Chapter
21, Sections 21.1, 21.2, 21.3, 21.4, 21.5 Thermochemistry
Chapter 22, Sections 22.1, 22.2, 22.3, 22.4,
22.5 Electrochemistry |
| Take
Exam: |
Exam
5 |
| Note: Complete
Solutions, including all units of measurement, must be done for all problems. |
[Top]
|