|
|
| Goal
I. Write and interpret equations for nuclear reactions. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal
I, you must be able to:
-
distinguish between
a chemical reaction and a nuclear reaction.
-
classify given nuclear
reactions with respect to the nuclear process represented, and the mode of radioactive decay (Table 24.2)
-
distinguish between
an induced nuclear reaction and a radioactive decay process.
-
complete an equation
for a nuclear reaction which has a missing reactant or product .
[Top]
| Goal II. Understand the
basic concepts underlying the model for nuclear decay and induced nuclear
reactions. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal
II, you must be able to:
-
describe the mechanisms
by which the emission of radiation is detected by a Geiger counter, a scintillation
counter and by a solid-state ionization detector.
-
relate the activity
of a radioactive sample to its rate of decay.
-
use the mathematical
model of first order kinetics to calculate half-life, rate constant, rate
of decay, time and/or amount of sample remaining for a given radioactive
decay process.
-
interpret a graph
of neutron number vs. proton number for the known nuclides (Figure
24.2) with respect to:
-
the “band of stability,”
-
predicting activity in terms of half-life,
-
predicting the mode of radioactive decay,
-
consequences of odd or even numbers of nucleons for
stability of isotopes.
-
interpret a diagram
illustrating a radioactive decay series. (Figure 24.3)
[Top]
| Goal III. Apply the principles
underlying the energetics of nuclear reactions . |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal
III, you must be able to:
-
use the Einstein
equation, E = mc2 (or
 E
= E
=  mc2)
to calculate the energy of a given nuclear reaction. mc2)
to calculate the energy of a given nuclear reaction.
-
calculate the mass
defect of a given nuclide and convert
mass defect into nuclear binding energy per nucleus and per nucleon.
-
interpret a graph
of binding energy per nucleon vs. mass number (Figure 24.13).
-
describe the process
of nuclear fission.
- describe and compare the
process of nuclear fusion with nuclear fission.
[Top]
| Goal
IV. Interpret and translate between complete structural, condensed
structural and line formulas for organic compounds and selected types
of isomers. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal IV,
you must be able to:
- distinguish between straight
chain and branched chain hydrides
of carbon (hydrocarbons) writing complete structural formulas from condensed
structural formulas and vice versa.
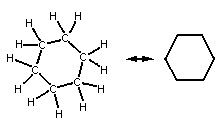
- define and recognize constitutional
isomers or structural isomers. Table 15.3.
[Top]
| Goal V. Recognize and correctly
name simple hydrocarbons and compounds containing common organic
functional groups. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal V,
you must be able to:
- distinguish among alkane (p. 623),
alkene (p. 628) and alkyne (p. 31) hydrocarbons.
- memorize the prefixes
associated with carbon chains from one to ten carbon atoms in length.
- identify and name the main
chain in an alkane and any side chain alkyl groups.
- memorize the names
and formulas for the common functional groups (Table 15.5.)
- define the term aromatic with
respect to the structure of an organic compound (p.632).
[Top]
| Goal VI. Understand the
fundamentals of polymer formation and the control of polymer properties. |
Objectives: To meet the requirements of Goal VI,
you must be able to:
- recognize formulas
for the monomer units and abbreviated polymer formulas (Table 15.6)
- explain the
process of chain polymerization by:
- defining chain reaction, initiator, chain
propagation, chain termination;
- diagramming (with chemical formulas) the
sequence of steps in the process (Fig. 15.25).
- explain the
difference between addition polymers and condensation polymers.
[Top]
|
Unit 6 Assignments |
Objectives
1 through 15
Text:
Video Programs: |
Chapter 24: pp. 1044-1081
21. Nuclear reactions I
22. Nuclear reactions II
23. Nuclear reactions III |
Objectives 16
through 25
Text:
Video Programs: |
Chapter 15: pp. 616-632, 639, 650-653
24. Organic nomenclature and compound classification
There is no video tape 25
26. Polymers |
| Textbook
Assignments: |
Read and
Understand all "Sample Problems," "Follow Up Problems" and select any 5 blue-colored problems at the end of the chapters.
The answers
for the Follow Up Problems are at the end of the chapter; the answers for
the blue-colored problems are in Appendix E. |
| Mandatory ChemSkill Builder Assignments to be submitted for grade (Scores of 80% or higher on each section will receive full credit): |
Chapter
23, Sections 23.1, 23.2, 23.3, 23.4, 23.6 Nuclear
Chemistry NOT 23.5
Chapter 24, Sections 24.1, 24.2 Organic Chemistry
Chapter 25, Sections 25.1, 25.2 Polymers |
| Take Exam: |
Exam 6 |
| Note: Complete
Solutions, including all units of measurement, must be done for all problems. |
[Top]
|