Performance
Learning objectives are student-centered. They describe the desired student performance.
Student Performance vs. Instructor Performance
One of the common mistakes made when writing learning objectives is to describe what instructors want to teach instead of what students are expected to be able to do upon their completion of a unit of instruction. It is important to differentiate between student performance and instructor performance.
 Example
Example
Let's take a look at the statement below.
|
Help students to understand the foundations of western culture and society. |
This statement describes what instructors will do. It tells us the topics that should be included in the instruction but it doesn't tell us what students are expected to be able to do. To revise this statement to a learning objective, we should rewrite it from student perspective. It will read:
|
Students should be able to explain the foundations of western culture and society. |
Bloom's Taxonomy and Measurable Verbs
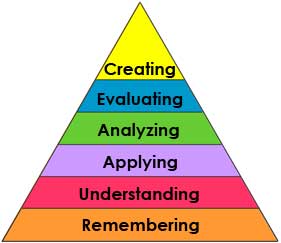
Bloom developed six categories of intellectual skills in the cognitive domain in 1956. A group of cognitive psychologists led by Lorin Anderson updated the taxonomy during the 1990's. You can find the six categories in the pyramids below, starting from the simplest behavior at the bottom to the most complex at the top. That is, the bottom ones must normally be mastered before the higher ones can take place. In order to teach students higher order thinking skills, basic knowledge should be provided first. Before we ask students to apply, analyze, evaluate, and extend what they are learning, we should make sure students can clarify their understanding and practice recall. Rewardingly, critical thinking exercises can deepen students' understanding and help them recall what they have learned.
|
Old Version |
New Version |
|
Overbaugh, R. C., & Schultz, L. Bloom's Taxonomy. Retrieved from Old Dominion University website: http://ww2.odu.edu/educ/roverbau/Bloom/blooms_taxonomy.htm |
|
Measurable verbs are the verbs that describe the actions that can be observed. In other words, measurable verbs refer to specific activities that we can observe a student doing.
Most of our courses fall into the cognitive domain. We should refer to Bloom's Taxonomy and select measurable verbs when we describe student performance, which can help us focus on specific cognitive processes and use correct measurable verbs. Bloom's Taxonomy and Verbs found on Paul D. Camp Community College's web site is a good resource for us to refer to when preparing our learning objectives. It associates different measurable verbs with each level of the taxonomy.
 Example 1
Example 1
|
Students will learn how to evaluate outside sources of information. |
"Learn" is not a measurable verb. We can observe a student reading an article or searching for information on the Internet, but we can't observe a student learning something. It is not possible for us to decide on the cognitive development process that the verb "learn" refers to. Thus, there is no way for us to come up with an assessment tool to evaluate students' mastery of this learning objective.
To make this learning objective a useful learning objective, we can revise it to,
|
Students will be able to evaluate outside sources of information. |
 Example 2
Example 2
|
Students will be able to list the four characteristics of effective leadership and explain how to develop leadership skills. |
This learning objective uses measurable verbs. We can observe a student listing the characteristics and explaining things. However, "List" and "explain" refer to two different levels of learning. Listing the four characteristics can measure if students can recall the information. It refers to the Knowledge level on Bloom's Taxonomy. "Explain" requires students to understand the ideas and the concepts. It refers to the Comprehension level on Bloom's Taxonomy, which is higher than Knowledge level. Like we said, a learning objective should focus on specific cognitive process and use a simple sentence. To make this learning objective clearer, we should break down the task. It is OK to use two or even three sentences to adequately describe a learning objective.
So this learning objective can be revised to,
|
Learning Objectives vs. Learning Activities
A learning objective describes a learned capability which is not a one-time event. When writing learning objectives for a unit of instruction, we usually start from the sentence "upon your successful completion of this lesson, you will be able to". Learning activities are the learning experiences that provide students the opportunity to practice the desired skills. They are different.
 Example
Example
|
Students will write an essay on one of the major theories of the cause of glaciation. |
This statement describes a learning activity that can help students better understand the major theories of the cause of glaciation, so the desired skill that students are expected to acquire is to understand the major theories of the cause of glaciation. So the learning objective should be:
|
Upon your successful completion of this lesson, you will be able to explain the major theories of the cause of glaciation. |
Remember the following principles when describing student performance:
|
Principles for Describing Student Performance |
|---|
|
Additional Resources
A Model of Learning Objectives was developed based on the revised Bloom's Taxonomy by the Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching of Iowa State University. It is a good visual presentation that visualizes the relationship between the levels of the cognitive development process and the knowledge dimensions. You may also want to refer to Bloom's Taxonomy by Carnegie Mellon University which briefly explains the knowledge dimensions and the levels of the cognitive development process.
Bloom's Taxonomy - Designing Activities tutorial developed by Colorado Community Colleges Online describes a variety of activities at each level of the revised Bloom's Taxonomy. You may refer to it when writing your own learning objectives. It can help you align your activity with a specific level of cognitive development process.
If you want to know more about affective domain and psychomotor domain, you may refer to Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains. This is a good review of different taxonomies in the three different learning domains, cognitive domain, affective domain, and psychomotor domain.
Self-Check Quiz